Understanding Gum Recession and Pyorrhea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
Oral health is critical to overall well-being, often indicating systemic health issues. Two conditions that mainly affect the gums are gum recession and pyorrhea (also known as periodontitis). Although they may appear similar, there are crucial differences between them in symptoms and treatment. Understanding these conditions can empower individuals to seek timely medical intervention and maintain optimal oral health.
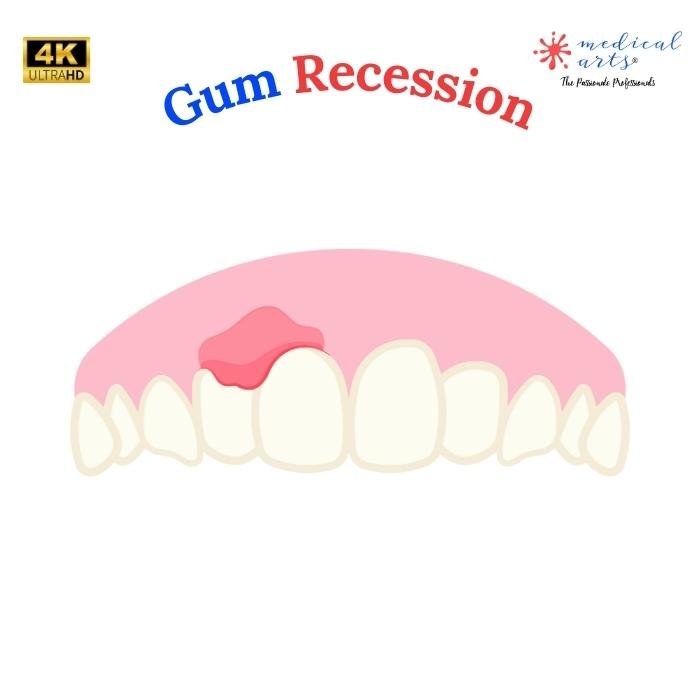
What is the Gum Recession?
Gum recession refers to the pulling away or shrinking the gum tissue, exposing more of the tooth or its root. It's a progressive condition that can go unnoticed until it becomes more severe. Over time, gum recession can increase sensitivity, tooth decay, and tooth loss.

Causes of Gum Recession
-
Improper Oral Hygiene: Lack of regular brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, triggering gum recession.
-
Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard can cause gums to recede.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Some people are more susceptible due to their genetic makeup.
-
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, like those occurring during pregnancy or menopause, can make gums more vulnerable.
-
Smoking and Tobacco Use: These habits contribute to plaque, which can lead to gum recession.
Symptoms
-
Increased tooth sensitivity
-
Longer appearing teeth
-
Notches or 'pockets' forming near the gum line
-
Inflammation and bleeding (in advanced cases)
What is Pyorrhea (Periodontitis)?
Pyorrhea, or periodontitis, is a severe gum infection that damages the soft tissue and destroys the bone supporting the teeth. It is an advanced form of gingivitis that can lead to tooth loss if untreated.
Causes of Pyorrhea
1. Poor Dental Hygiene: The primary cause is the buildup of dental plaque due to inadequate oral hygiene.
2. Smoking: Significantly increases the risk.
3. Underlying Health Conditions: Diabetes, HIV, and other immune-compromising conditions can contribute.
4. Medications: Some medications can cause dry mouth, reducing saliva and increasing vulnerability to periodontitis.
Symptoms
- Swollen or puffy gums
- Bright red, dusky red or purplish gums
- Bleeding gums
- Bad breath
- Pain while chewing
- Loose teeth or loss of teeth
Differences Between Gum Recession and Pyorrhea
Onset: Gum recession is usually gradual, whereas pyorrhea can progress more quickly.
Affected Area: Gum recession involves the gum pulling away from the teeth; pyorrhea damages gums and underlying bone.
Treatment Complexity: Pyorrhea often requires more aggressive treatment, including surgery and antibiotics, whereas early-stage gum recession might be managed through improved oral hygiene.
Vocabularies:
-
Scaling and Root Planning: A deep cleaning technique.
-
Gum Grafts: In severe cases, a surgical procedure to replace receded gums.
-
Improved Oral Hygiene: Brushing and flossing correctly.
-
Antibiotic Treatment: To control bacterial infection.
-
Flap Surgery: To remove tartar deposits in deep pockets.
-
Bone and Tissue Grafts: To regenerate lost bone and tissue.
Conclusion
Though gum recession and pyorrhea are both gum-related conditions, they differ in their causes, symptoms, and treatment. Maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and early intervention are vital for preventing and managing these conditions. If you notice signs of either, consult a dentist immediately for a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your needs.