Epidural Injection vs Epidural Anesthesia: What You Need to Know
When managing pain, inflammation or undergoing surgery, you might hear terms like "epidural injection" and "epidural anesthesia." Both involve placing medication in the spine's epidural space to relieve discomfort or block sensation, but they're used for different purposes and in other medical contexts. Let's break down these terms to understand better what they mean.

To read more about Spinal anesthesia check >> "Spinal Anesthesia"
What is the Epidural Space?
Firstly, a little anatomy lesson: the epidural space is a space in the spine just outside the membrane that surrounds the spinal cord. Medication can be placed here to numb or block sensations.
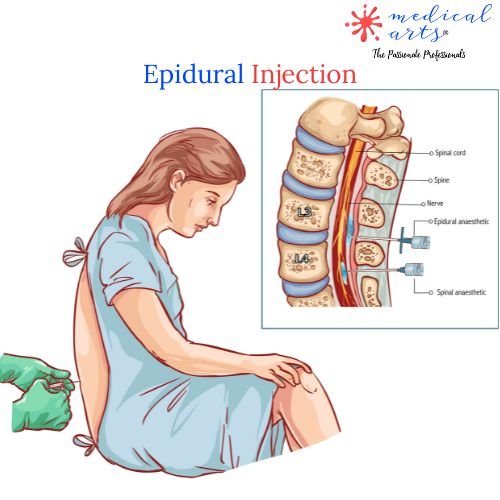
Epidural Injection
What Is It?
Epidural injections typically contain steroids and relieve back, legs, or arms pain. They are most commonly used for herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or sciatica.
How Does It Work?
The medication helps to reduce inflammation in the spinal nerves, providing temporary relief from pain. It's more of a therapeutic measure designed for symptom relief rather than complete numbing of an area.
Procedure:
- Location: Typically done in an outpatient setting.
- Duration: The procedure takes around 15-30 minutes.
- Anesthesia: Usually, local anesthesia is used to numb the injection site.
Recovery:
- Immediate: Some relief, but full effects may take a few days.
- Long-Term: Effects can last for weeks or months but are generally not permanent.
Epidural Anesthesia
What Is It?
Epidural anesthesia blocks sensation in a specific body area, usually during surgery or childbirth. It contains anesthetic agents, sometimes in combination with opioids, to block nerve signals.
How Does It Work?
It numbs a larger region than an epidural injection and is used for more invasive procedures, effectively blocking sensation from the waist down or in a specific area.
Procedure:
- Location: Usually administered in a hospital setting.
- Duration: Timing varies based on the type of surgery or childbirth process.
- Anesthesia: The epidural is the anesthesia, so additional numbing agents are not generally used.
Recovery
- Immediate: You'll regain sensation over a few hours as the medication wears off.
- Long-Term: Effects are temporary and wear off entirely once the medication is discontinued.
Key Differences
- Purpose: Injection is for pain relief; anesthesia blocks sensation during surgery or childbirth.
- Medication: Injection usually involves steroids; anesthesia uses anesthetic agents.
- Duration and Setting: Anesthesia is typically used for longer procedures in a hospital, while injections are often outpatient and shorter.