Anxiety Disorders - DSM-5 - Definition, Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatments, and Self-help.
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a human emotion and a normal stress reaction to an immediate threat or anticipation of future concern, and it can be beneficial in some circumstances. Some situations that trigger anxiety range from a problem at work to a mere idea of uncertainty about the future. Anxiety serves to alert us to danger and help us be more vigilant and prepared.
Everyone experiences it to a different degree. When it repeatedly gets out of control, it becomes a disorder.
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental disorders and affect nearly 30% of adults at some point in their lives.
What anxiety disorders are in the DSM 5?
Anxiety disorders are a group of anxiety-related mental health problems. Each of those disorders has specific features and is treated accordingly.
Anxiety Disorders that are part of the DSM 5:
Specific phobias are irrational fears of a specific object or situation.
Social phobia, the overwhelming concern of being humiliated or embarrassed in social situations.
Panic disorder is a sudden, intense feeling of fear that brings anxiety in its most severe form.
Agoraphobia, the fear of being in a place where it is difficult to escape if needed.
Generalized anxiety disorder is an exaggerated feeling of uneasiness impending doom.
Separation anxiety disorder persistent worry of losing the person to which they are attached.
Selective mutism. Anxiety in which young kids stop talking with their family in public, like at school.
Click on the image below to get your instant copy of DSM-5-TR PDF 2023
Signs and symptoms of anxiety disorders.
The signs and symptoms of anxiety can widely vary among people and across anxiety disorders. However, we recognize some signs that are more frequent than others, and To simplify them, we split them into three different components.
THE PHYSICAL SIGNS are increased heart rate, shakiness, sweating, difficulty breathing, Digestive Disturbances, and chest pressure.
The second component is COGNITIVE, the inability to concentrate and process thoughts normally, anticipating the worst possible outcome.
the third COMPONENT is BEHAVIOURAL, seeking drug and alcohol abuse, irrational overprotective behaviors that affect the person's life.
What are the causes and risk factors of an anxiety disorder?
Not all causes of anxiety are currently known, but researchers have pointed at some situations that may be the cause or contribution to the development of uncontrolled anxiety.
A combination of genetic and environmental conditions increases the odds of developing anxiety disorders, and here are some other factors:
Chemical substances like medications, drug abuse, or drug withdrawal. Environmental stressors include a pandemic, wars, and natural disasters. medical conditions, mainly that affect our glands, such as the thyroid.
Traumatic events, childhood abuse, adverse life experiences, severe illness. And personal traits such as low self-esteem.
How anxiety disorders are diagnosed ?
Diagnosis of anxiety disorder counts on the clinical presentation and history of the disorder. Sometimes an anxiety disorder goes undiagnosed because the person believes it is just worrying and not a medical condition.
Based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, an anxiety disorder is associated with at least three of the following signs.
Restlessness, Easily fatigued, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension or, sleep disturbance.
![]()
However, confirming the condition and knowing the cause requires a lengthy process of physical examinations that may include blood tests and imaging to rule out underlying medical conditions. in addition to a Mental health evaluations and psychological questionnaires.
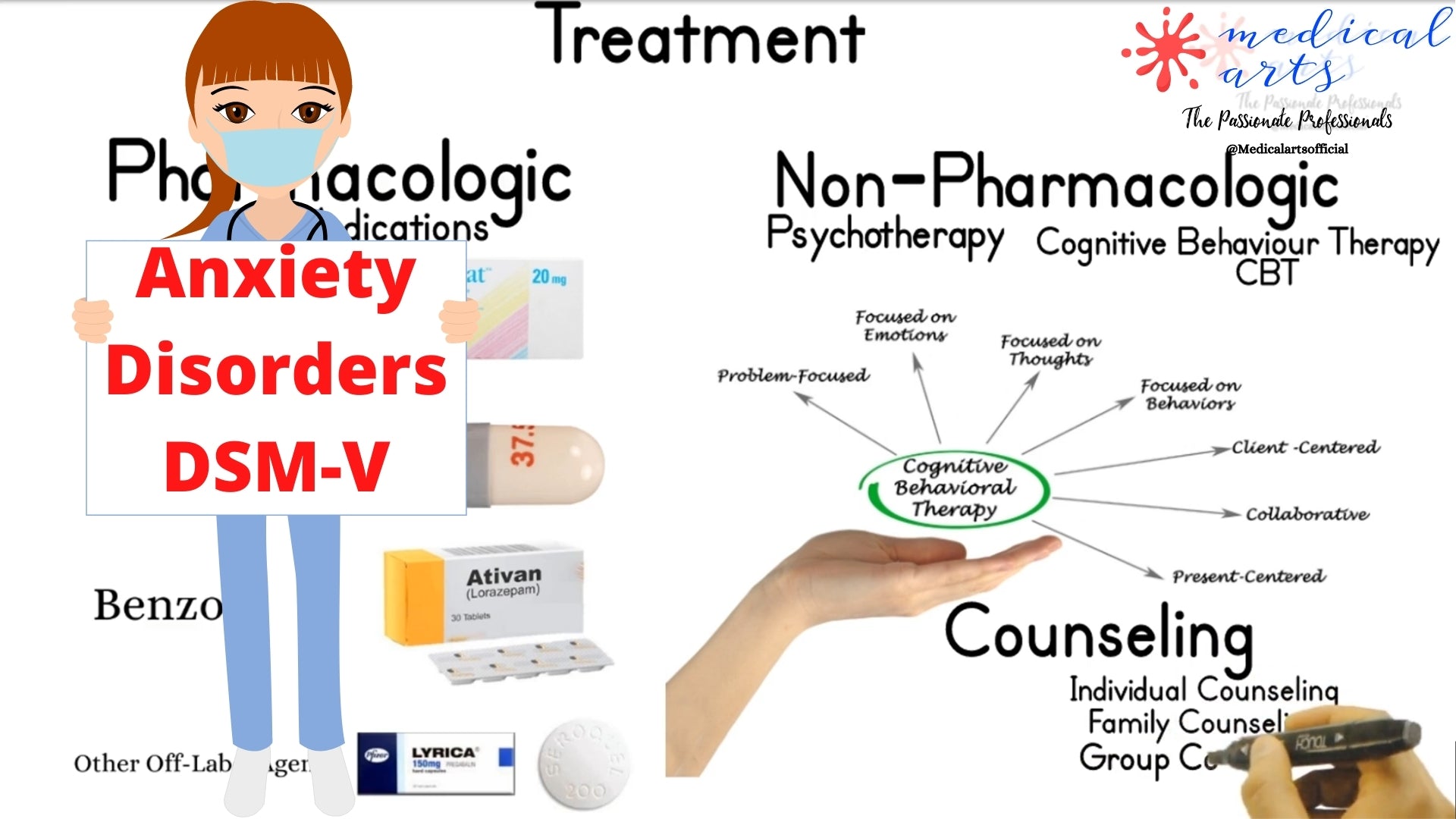
Can anxiety disorder be treated? How to manage anxiety disorders?
Although each anxiety disorder has unique characteristics, most respond well to two types of treatment:
Pharmacological, which contains multiple groups of medications that help decrease the signs and symptoms of anxiety. They often bring back productivity to people who have lost their normal function in society.
The other treatments are called non-pharmacological, this include psychotherapy or also called talk therapy, a treatment that can be effective to ease stress, provide a new perspective on problems,
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, a treatment that focuses on thoughts and behaviors, teaches people different ways of thinking, behaving, and reacting to anxiety-producing and fearful objects and situations.
Counseling is another effective way to manage anxiety disorders. It is to help the concerned person through purposeful conversation and guidance to resolve problems.
Prevention is always easier than dealing with late complications.
By starting to experience signs and symptoms of anxiety, The person suffering from anxiety can take action based on their specific strategy containing one of the following tools.
Relaxation techniques,
Physical exercising,
Taking a deep breath.
Talking to someone willing to listen to them might be a friend, a therapist, or a family member.
Stress management techniques and meditation can help people with anxiety disorders calm themselves and may enhance the effects of therapy.
More resources:
www.nimh.nih.gov
www.anxietycanada.com
www.adaa.org
www.psychiatry.org