We are going to explore the accessory structures that connect to our digestive system. Please note that This is a continuation of our previous video, titled “GI tract.” Which makes up the other component of our digestive system.
There are Three accessory structures in the oral cavity: the teeth, salivary glands, and tongue.
And Three other accessory organs in the abdominal cavity connect to the first segment of the small intestine. They are the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder.
In the oral cavity, mechanical digestion of the ingested food starts with mastication achieved by teeth which change the structure of the food to become a bolus. The chemical reaction that occurs via enzymes in the saliva contributes to this transformation also. A 3rd structure is a tongue, which assists in the formation and mostly in swallowing the bolus.
Teeth are collectively called dentition.
Generally, at the age of 17, we have Thirty-two permanent teeth arranged in a predictable sequence.
Human teeth include variation and are called incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
Teeth decay is one of the most common diseases. The rate of tooth decay decreases after age 35. However, then problems with the gums may develop.
Tongue is formed from skeletal muscle. It manipulates the food to assist in chewing and forming the bolus by compressing the partly digested materials.
thousands of chemoreceptors on the surface of the tongue recognize the variety of tastes like salty, sour, bitter, sweet, savory
The salivary glands are three pairs of structures that secrete their saliva via linked ducts to the oral cavity.
The parotid glands are located in front of the ears produce watery serous liquid carrying salts and enzymes. Secrete about 25-30% of the saliva.
The SUBMANDIBULAR glands, also called SUBMAXILLARY, located below the jaw secrete watery serous fluid with some mucus. Produce most of the saliva about 60-70%.
The sublingual glands are located under the tongue secrete thick, sticky mucus and contain salts and salivary amylase. Contribute only about 3-5% of the total saliva.
Saliva is 99% composed of water. A small amount of it is continuously produced to ensure that the oral cavity and its structures remain moist and clean.
Other components in saliva are
enzymes such as amylase, which breaks down complex carbohydrates.
Bicarbonate found in saliva helps to maintain a neutral PH.
Lysozyme and antibodies kill bacteria.
Other substances are also found, such as electrolytes and MUCIN.
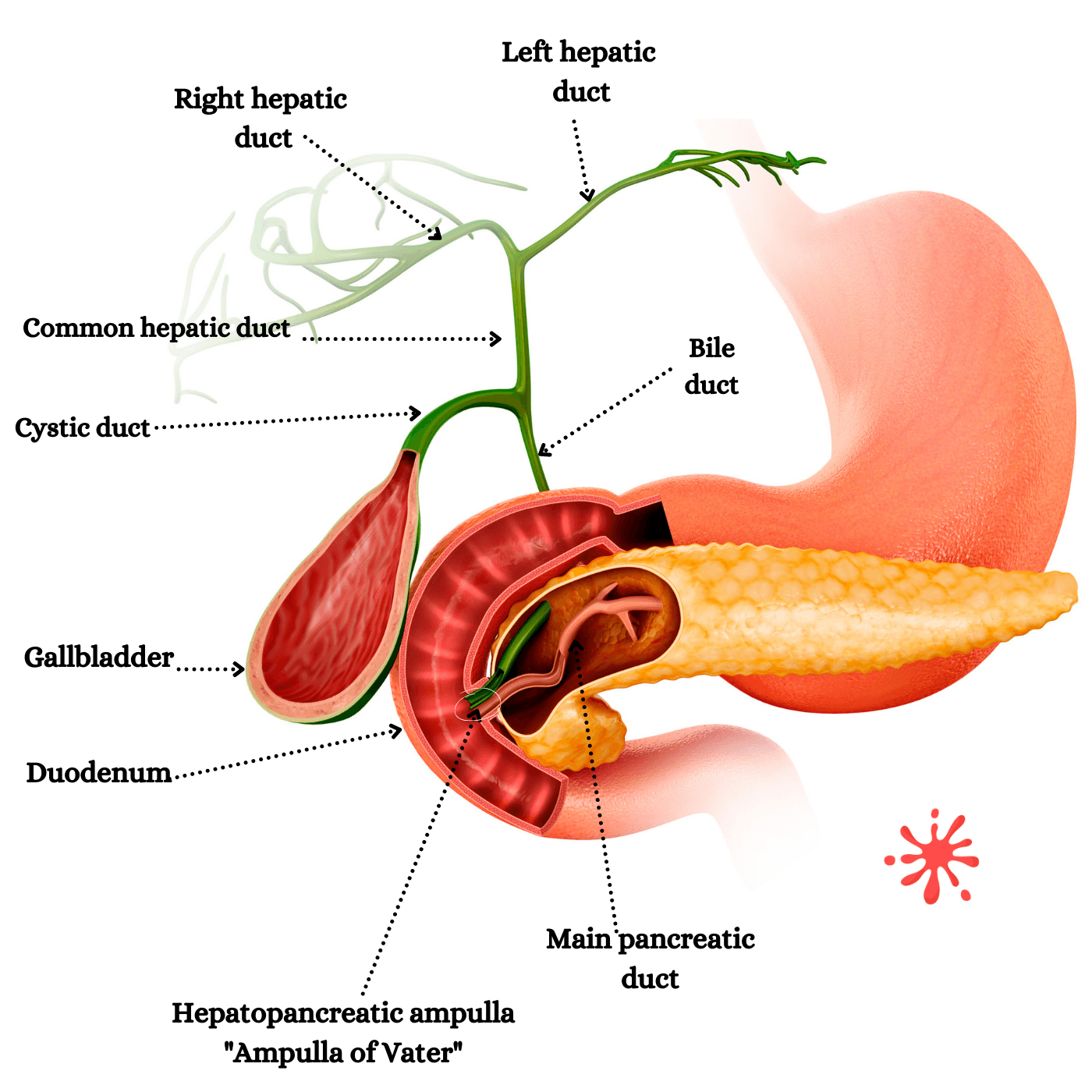
Three Accessory digestive organs assist in the chemical breakdown of food by secreting their enzymes into the first segment of the small intestine, the duodenum.
The liver produces and releases its bile into the gallbladder by multiple thin tubes.
Then the concentrated bile in the gallbladder gets carried through the common bile duct, where it meets the pancreatic duct. These two tubes form the ampulla of Vater.
The liver is located Underneath the diaphragm.
It is composed of four lobes, the left, and right, then two other lobes that are found at the inferior angle of the liver are the caudate and the quadrate lobes.
It receives nutrient-rich blood from the guts via the portal vein makes 75-85% of the blood flow to the liver. The remaining blood flow is supplied by the Hepatic artery.
The liver carries one of the most diverse functions in our body, ACTS as a gland. It also detoxifies the blood, serves as storage, and contributes to the immune system.
The liver will be discussed in detail in another video. Today We will focus on its role in the digestive system.
The liver itself is not necessarily a gland. However, part of its tissues is exocrine glands, which secrete their substances in a cavity. In the case of the liver, it produces and releases its bile in the gallbladder.
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped sac, about 4 inches long.
The liver drains its bile into the hepatic ducts toward the gallbladder. Concentrated bile of approximately 40 to 60ml is on standby for the next fatty meal.
After a meal, the gallbladder squeezes the stored bile into the intestine to digest fat and enhance the absorption of liposoluble vitamins.
Cholecystectomy is a surgical operation consist of the removal of the gallbladder.
In a post-cholecystectomy, Instead of concentrating the bile in the gallbladder, the bile flows directly into the intestine anytime the liver produces it.
Not as much bile will be secreted after ingesting a meal, but enough to allow digestion.
The pancreas is a soft 6 inches long organ situated behind the stomach and is connected by a duct to the duodenum.
It is divided into four parts, the head, neck, body, and tail.
Similar to the liver, the pancreas performs both functions as endocrine and exocrine secretions. The exocrine cells occupy the majority of the pancreas. They serve digestion by secreting enzymes such as lipase, trypsin, and amylase. Bicarbonate is also produced and released by the pancreas. The secretions are collectively called pancreatic juice.