Welcome back to another juicy episode from medical arts official, today we are going to break down the most complex system of our body, it is the NERVOUS SYSTEM!
Can we live without our nervous system? The nervous system is the center of operations to all of our body organs, DID YOU! think the heart is what makes us ALIVE? Well, think again; the nervous system is what makes the heartbeats. All the daily activities, from working to practicing our hobbies and experiencing emotions, are all ruled and controlled by our nervous system.
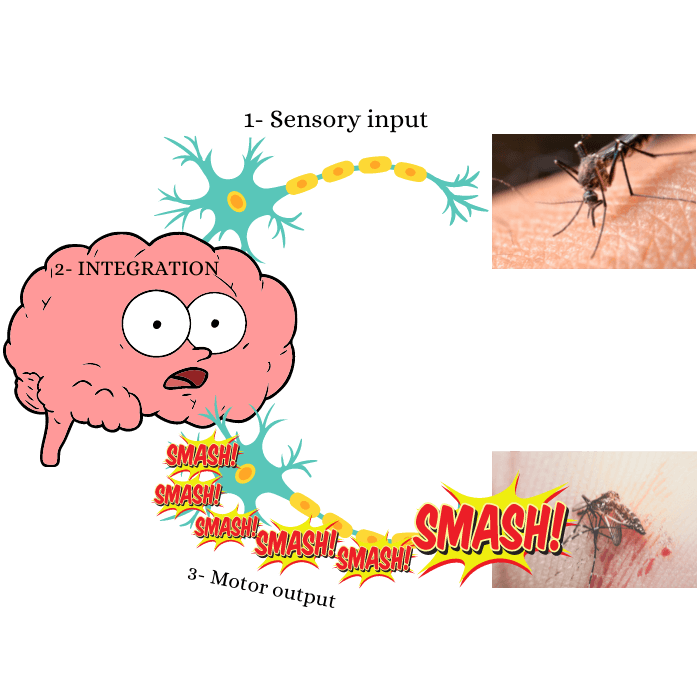
With all the complexity of this system, we can conclude three main functions. First is Receiving information, analyzing this information, taking the proper reaction. The technical words for each step of the process are as follow SENSORY INPUT! It can be internal, like pain or cramps. or external, like tickling and heat. Such stimuli will be encoded and transported to the central nervous system to analyze it; we call this process INTEGRATION! The next step is the reaction; we call it MOTOR OUTPUT! the message will be delivered to the proper tissues in the muscles and skeletal system to carry the order like the hand smashed that irritating mosquito! This phase can be voluntary or involuntary.
The structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM consists of 2 major DIVISIONS. the central nervous system. It is also made of 2 major parts. THE BRAIN! The brain itself is composed of 2 hemispheres and multiple regions. The other part of the central nervous system is THE SPINAL CORD! Only the portion of the spinal cord in red in the graphics belongs to the CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM! the other division is PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. It consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves plus 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Those nerves serve two other subdivisions. The first subdivision is the SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM! the other subdivision is the AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM! the latter is involuntary. It is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. each division and subdivision will be explained in detail in a separate crash course.
Nerve cells are of two types. NEURONS! and GLIAL CELLS! Neurons are the functional unit of the nervous system. They do transmit the messages back and forth from sensory input and to motor output. Each neuron is made of 2 main elements. a CELL BODY! also called soma. And of PROCESSES. Processes are the extensions that branch off the cell body. If those processes bring impulses inside the cell, we call them DENDRITES! They are shorter extensions than axons. The other type of process is called the AXON!, which conducts impulses AWAY from the cell.
Glial cells. Cannot transmit nerve impulses. They are smaller than neurons and ten times more numerous. unlike neurons. gliaL cells are capable of mitosis, which means they do regenerate after an injury. They account for about half the volume of the entire nervous system.
Astrocytes, are the most extensive glial cells. Star-shaped, support and nourish neurons. It forms the blood-brain barrier. It replaces damaged neurons.
OLIGODENDROCYTES! smaller than astrocytes. Maintain and produce myelin in the central nervous system.
MICROGLIAL CELLS! The smallest percentage of glial cells. Spider-like shape moves in response to infections and disposes of debris.
EPENDYMAL CELLS! Contributes to the formation of the CSF. It covers the lining of the central canal and assists in the function of the blood-brain barrier.
We are done with the four glial cells of the central nervous system; we have two more glial cells that exist in the peripheral nervous system. THE SCHWANN CELLS. Those cells do a similar function that the oligodendrocytes do in the central nervous system. The last glial cells are called SATELLITE CELLS! They are flattened cells with the same functions as the astrocytes.
Functions can classify neurons, but now we will look at their different structures first. UNIPOLAR! are the sensory neurons in the peripheral nervous system. PSEUDO UNIPOLAR! is found in the SENSORY ganglia of some cranial nerves. BIPOLAR NEURONS! are rare and limited to the nerves of the eyes and ears. MULTIPOLAR NEURONS!
Are the most numerous, and they are the majority of the motor neurons in our body. The names are given to each neuron type based on how many processes, dendrites, and axons are attached to the cell body.
We recognize three different types of neurons based on their functions. The SENSORY division is the neurons that enter the cell body, also called AFFERENT NEURONS! they serve the SOMATIC senses such as taste, pain, and vision. They make part also of the VISCERAL sensory system. This includes detection of a fever or a stretch in the wall of organs. This translates into pain for a person suffering from a heart attack or appendicitis. The second division of neurons is the MOTOR! also called THE EFFERENT! the motor neurons! Serve both the somatic system. which is a voluntary action. And the Visceral! The system is what controls our heartbeats and involuntary breathing. Finally, THE INTER NEURONS! is found in the neural pathway in the central nervous system. It facilitates communication between the sensory and motor neurons.
Here are some facts about the nervous system before we close the curtains. Neuron cells are not replaceable after birth. The brain consumes up to 60% of the body's glucose at rest, as it does not have an energy reserve. The brain reaches maximum weight when we are young adults. After that age, you better take care of it!