The Role of Earwax: A Natural Cleanser
Earwax, often perceived as inconvenient, plays a crucial role in ear health. This sticky substance, scientifically known as cerumen, serves as a natural cleanser, gradually moving outward from the inner ear canal, gathering dead skin cells, hair, and dirt along the way. Remarkably, earwax even possesses antibacterial and antifungal properties.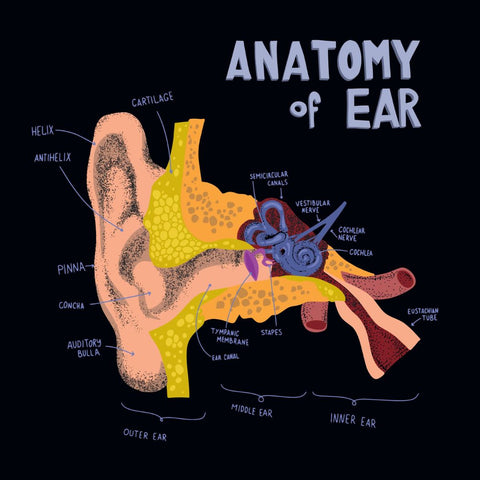
When Earwax Overstays.
However, excessive earwax can lead to various complications. A blocked ear canal may result in earaches, infections, and, surprisingly, even a cough by stimulating the vagus nerve. Hearing loss is another potential consequence.
To Remove or Not to Remove?
The American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery advises a cautious approach, suggesting removal only when earwax causes problems. Determining the source of an issue can be challenging without removal.
Understanding Earwax Development
Earwax, or cerumen, originates from the combined secretions of sebaceous and sweat glands in the outer ear canal. Jaw movement propels these secretions to the ear opening, where they naturally flake off.
Factors Leading to Stubborn Earwax
Earwax can become dry and complex over time, increasing the risk of blockage. Conditions like eczema and age-related changes in glandular secretions can contribute. Genetics also play a role, with dry earwax more common in some populations, like East Asians.
Safe Earwax Removal Methods
Removing earwax can be done by a healthcare professional or at home. Avoid cotton swabs, which can push earwax deeper.
Instead, tilt your head, introduce a few drops of water, saline solution, or hydrogen peroxide, and let gravity do the work. Use a bulb syringe if needed, but avoid this method with a damaged eardrum.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Over-the-counter eardrops can help break up earwax, with water-based and oil-based options available. Studies show both types are effective. Consult a clinician if you need clarification.
Hearing Aid Users Beware
Hearing aids can disrupt the natural migration of earwax, potentially leading to increased secretion and damage to your device. Regular check-ups with your clinician are advisable if you wear hearing aids.
Understanding the delicate balance of earwax management is vital to maintaining ear health and preventing unnecessary discomfort.