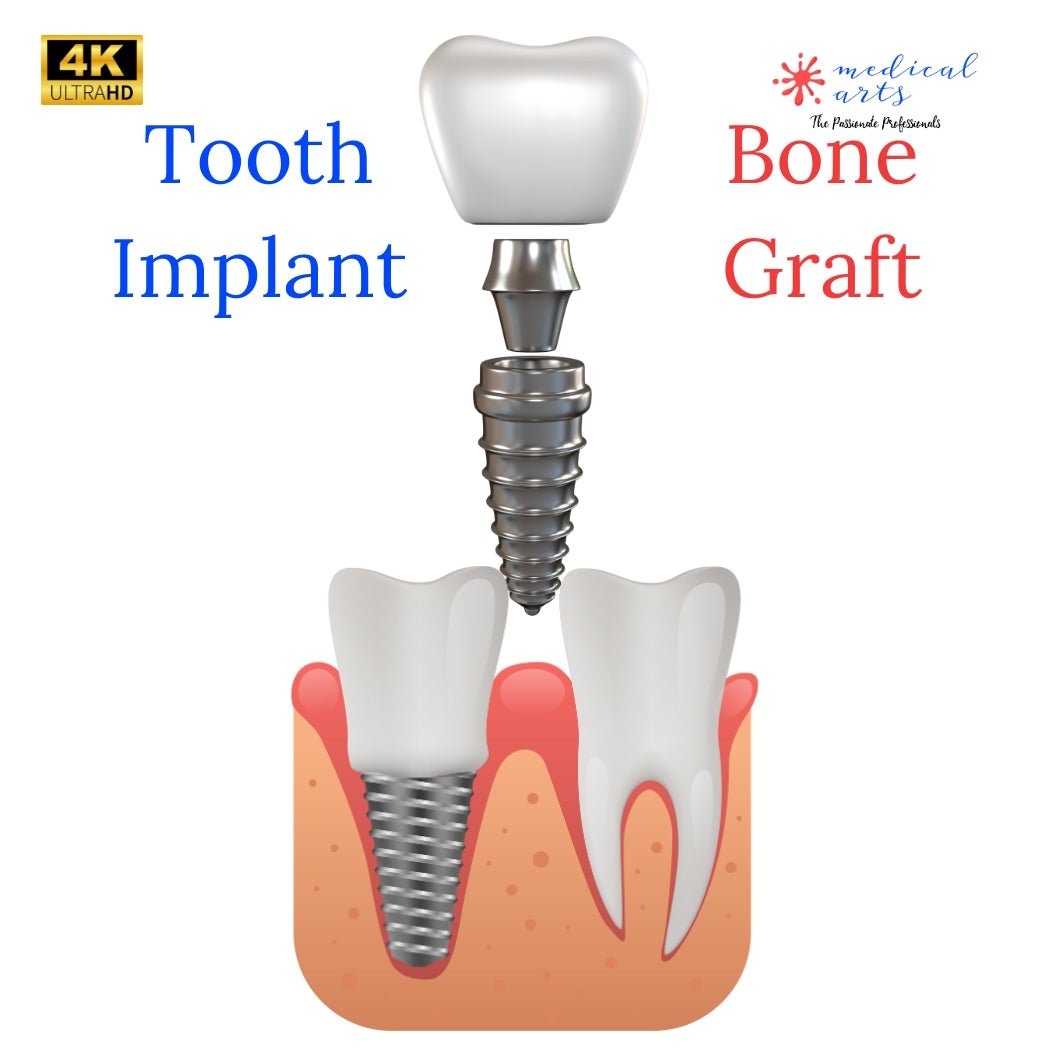
The Role and Techniques of Bone Grafting Augmentation Using Bone Blocks
Bone grafting augmentation is a crucial surgical technique used to repair or rebuild bones through the transplantation of bone tissue. This method is essential in various medical fields, including orthopedics, dentistry, and reconstructive surgery. Bone grafting using blocks of bone, in particular, offers a strategic approach for managing extensive bone loss due to trauma, disease, or congenital disabilities.
Understanding Bone Grafting Augmentation
Bone grafting is a procedure to restore the lost bone and support bone regeneration. It can involve several types of grafts, depending on the source of the bone graft material:
- Autografts: Bone harvested from the patient’s body, such as the hip or ribs.
- Allografts: Bone sourced from a donor or a cadaver that has been processed to ensure safety and compatibility.
- Xenografts: Bone derived from a different species, commonly from bovine sources.
- Synthetic Grafts: Man-made materials that mimic the properties of natural bone.
Among these, autografts are often considered the gold standard due to their higher success rates in terms of integration and reduced risk of immune rejection.
The Specifics of Using Bone Blocks
Bone block grafting is a specific bone grafting technique used primarily when there is a significant bone deficit. This method is particularly prevalent in dental implantology, where it rebuilds the alveolar ridge and provides sufficient bone for implant placement.
Surgical Procedure
The surgical procedure for bone block grafting can be summarized in the following steps:
- Preparation: The recipient site is prepared to receive the graft. This includes cleaning and possibly cutting a small bed in the existing bone to fit the block.
- Harvesting the Bone Block: If using an autograft, the bone block is typically harvested from the chin, jaw, hip, or tibia, depending on the size and shape needed.
- Transplantation: The bone block is then shaped and fixed to the deficient area using surgical screws.
- Healing and Integration: Over time, the transplanted bone integrates with the existing bone through osteointegration.
Advantages and Challenges
Advantages:
- Structural Stability: Bone blocks provide a solid, stable structure that can support implants or withstand forces in reconstructive sites.
- High Success Rate: Autologous bone blocks have a high rate of integration and a lower risk of rejection.
- Natural Regeneration: Supports new bone growth, enhancing the graft site's strength and functionality.
Challenges:
- Surgical Complexity: The procedure requires precise surgical skills and careful handling to avoid damaging the graft or surrounding tissues.
- Recovery Time: Patients may experience longer recovery due to the procedure's invasiveness, primarily if the bone is harvested from areas like the hip.
- Potential for Complications: Risks include infection, nerve damage, or graft failure, which, although rare, are significant considerations for surgeons and patients.
Recent Advances and Future Prospects
Recent technological advancements have enhanced the efficacy and outcomes of bone block grafting. These include:
- Computer-Aided Design/Manufacturing (CAD/CAM): This technology is used to create precise and customized bone grafts from CT scans of the patient’s bone.
- Growth Factors and Stem Cells: Research is ongoing into using biological materials like growth factors and stem cells to accelerate bone healing and integration.
- 3D Printing: Emerging uses of 3D printing technology can fabricate bone blocks that match the defect site in shape and size.
Conclusion
Bone grafting using blocks of bone is a transformative technique that has significantly improved outcomes in reconstructive surgery, dentistry, and orthopedics. As research progresses, integrating innovative technologies promises even greater precision, reduced recovery times, and enhanced patient outcomes. By overcoming the challenges of significant bone loss, bone block grafting continues to be a cornerstone in surgical reconstruction, offering many patients hope and improved quality of life.